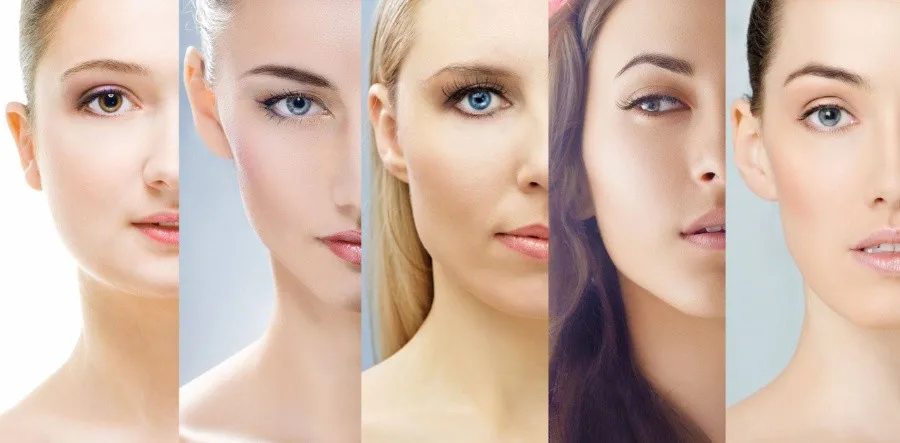
Identifying your skin type is crucial for choosing the right skincare products and creating a personalized routine. Regular observation and adjusting your routine based on your skin’s needs will help maintain healthy and radiant skin. Keep in mind that your skin type may change over time, so reassess periodically for optimal skincare. In summary, a proper face cleansing routine involves choosing the right products for your skin type, using gentle techniques, and incorporating the process into your daily and nightly skincare regimen. This practice contributes to the overall health and appearance of your skin by keeping it clean and ready to absorb the benefits of subsequent skincare products.

Here’s a detailed guide on how to identify your skin type:
Step 1: Cleanse Your Face
- Start with a clean face. Remove any makeup or skincare products you may be wearing using a gentle cleanser suitable for sensitive skin. Pat your face dry with a clean towel.
- Different skin types require different cleansers. For oily or acne-prone skin, a foaming or gel-based cleanser with salicylic acid may be suitable. Dry or sensitive skin may benefit from cream or lotion-based cleansers with ingredients.
- Consider avoiding cleansers with harsh chemicals or strong fragrances, as they can irritate the skin.
- Use lukewarm water to wet your face. Extremely hot water can strip the skin of natural oils, leading to dryness.
- Have a clean, soft washcloth or cleansing brush on hand for a deeper cleanse.
- Use lukewarm water to rinse your face, ensuring that all cleanser is completely removed.
- Pat your face dry with a clean towel. Avoid rubbing, as this can cause irritation.
- Cleanse your face twice a day – once in the morning and once before bedtime.
- Adjust your routine based on your skin type and specific skincare needs.
Step 2: Observe Your Skin's Feel and Texture
-
Normal Skin:
Proper maintenance through a balanced skincare routine helps preserve the natural beauty and health of normal skin. It is considered the ideal skin type, as it exhibits a harmonious combination of characteristics that contribute to a healthy and radiant complexion.
- Normal skin maintains optimal moisture levels, striking a balance between not being too oily or too dry.
- The skin’s natural barrier function is effective in retaining water, preventing excessive evaporation.
- Normal skin typically has a smooth and even texture.
- The surface is neither excessively rough nor overly soft, presenting a healthy and youthful appearance.
- Pores are generally small and not enlarged, contributing to the skin’s refined and even appearance.
- Normal skin has a moderate level of sebum production, preventing pores from becoming clogged or enlarged.
- Blood circulation is typically good, contributing to the skin’s vibrant and lively appearance.
- Normal skin requires a balanced skincare routine, including cleansing, moisturizing, and sun protection.

-
Oily Skin:
Understanding and addressing the specific needs of oily skin can help individuals manage its challenges effectively and maintain a clear and balanced complexion.
- Oily skin is more susceptible to acne breakouts due to the excess oil providing an ideal environment for acne-causing bacteria to thrive.
- Blackheads, whiteheads, and pustules are common manifestations of acne in individuals with oily skin.
- Oily skin is characterized by an overproduction of sebum, the natural oil produced by the sebaceous glands in the skin.
- Sebum plays a crucial role in maintaining skin health by keeping it moisturized, but excessive production can lead to oily skin.
- One of the most noticeable features of oily skin is the shiny or greasy appearance, especially in the T-zone (forehead, nose, and chin).
- Genetic predisposition and hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in determining skin type, including whether an individual has oily skin.
- Environmental factors, such as high humidity, can exacerbate oily skin. Hot and humid conditions can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil.
- Pollution and exposure to certain toxins in the environment may also contribute to skin issues in individuals with oily skin.
- An effective skincare routine for oily skin typically includes gentle cleansing to remove excess oil and debris.
- Striking a balance between keeping the skin clean and moisturized is solution for maintaining healthy skin despite its oily nature.

-
Dry Skin:
Dry skin is a common dermatological condition characterized by a lack of moisture in the outermost layer of the skin. It can occur for various reasons, and understanding its causes and symptoms is crucial for effective management. Here are some detailed points about dry skin:
Causes of Dry Skin:
-
Weather Conditions:
Exposure to cold, dry air, and low humidity levels can lead to moisture loss from the skin.
-
Hot Showers and Baths:
Prolonged exposure to hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, contributing to dryness.
-
Harsh Soaps and Cleansers:
Using harsh soaps and cleansers can disrupt the skin's lipid barrier, leading to dryness.
-
Age:
As individuals age, the skin tends to produce fewer natural oils, making elderly people more prone to dry skin.
-
Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and hypothyroidism can contribute to dry skin.
Lifestyle and Skincare Habits for dry skin:
-
Balanced Diet:
Consuming a diet rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals promotes overall skin health.
-
Balanced Diet:
Consuming a diet rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals promotes overall skin health.
-
Sun Protection:
Using sunscreen helps protect the skin from harmful UV rays, preventing further damage.
-
Clothing Choices:
Wearing breathable fabrics and avoiding tight, restrictive clothing can reduce irritation.
Symptoms of Dry Skin:
- Itching: Dry skin is often accompanied by itching, which can be mild to severe.
- Flakiness: The skin may appear flaky or develop small, fine cracks.
- Redness: Dry skin can become red and irritated, especially in more severe cases.
- Tightness: The affected skin may feel tight and uncomfortable.
- Rough Texture: Dry skin can have a rough and uneven texture.

Combination Skin:
Combination skin is a unique skin type characterized by the coexistence of different skin conditions in various areas of the face. This skin type presents a combination of both oily and dry regions, making it challenging to find a one-size-fits-all skincare routine.
Oily T-Zone:
The T-zone, comprising the forehead, nose, and chin, is prone to excess oil production. This excess sebum can lead to enlarged pores, blackheads, and occasional acne breakouts.
Dry or Normal Cheeks:
The cheeks, on the other hand, may experience dryness or maintain a normal skin texture. This can result in flakiness, tightness, or rough patches, especially during changing weather conditions.
Seasonal Changes:
The characteristics of combination skin can change with the seasons. For instance, during colder months, the dry areas may become more pronounced, while the T-zone might remain oily. In warmer weather, oiliness in the T-zone may increase.
Step 3: Check for Sensitivity
Sensitive Skin:
Sensitive skin is a condition that many individuals experience, characterized by heightened reactivity to various environmental factors, skincare products, or other stimuli. This skin type often requires special attention and care to prevent irritation and discomfort. Sensitive skin refers to a skin type that is more prone to reactions such as redness, itching, burning, or stinging.
Skincare Routine:
- Cleansing: Use a mild, fragrance-free cleanser suitable for sensitive skin.
- Moisturizing: Regularly moisturize to maintain the skin’s hydration levels and strengthen the skin barrier.
- Sunscreen: Sensitive skin is often more susceptible to sun damage. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF to protect the skin from UV rays.
- Avoiding Irritants: Limit exposure to known irritants, such as strong winds, extreme temperatures, and harsh fabrics.
- Patch Test: Before using a new skincare product, perform a patch test to check for any adverse reactions.
Step 4: Assess for Aging Signs
Loss of Elasticity:
Wrinkles and Fine Lines:
Aging skin commonly develops wrinkles and fine lines due to a combination of factors, including decreased collagen production, reduced skin cell turnover, and exposure to environmental factors such as sunlight and pollution.
Thinning of the Skin:
Aging skin undergoes a thinning process, primarily due to a decrease in the production of underlying supportive structures. Aging skin may experience a loss of fat and volume, especially in the face. This can result in a hollowed appearance, accentuating the prominence of wrinkles and fine lines.

Step 5: Analyze Breakouts
Acne-Prone Skin:
Acne-prone skin is a common dermatological condition characterized by the development of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and other types of blemishes on the skin. Gentle cleansing helps remove excess oil and prevent pore blockage. Oral or topical antibiotics can control bacterial growth. Common characteristics include the presence of pimples, pustules, cysts, blackheads, and whiteheads. If you’re seeking natural remedies, consider exploring our guide on Introducing Homemade Remedies for Bright Skin.
Causes of Acne:
- Excess Sebum Production: Overproduction of sebum, an oily substance, can clog pores and contribute to acne.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, can trigger acne.